Table of Contents
introduction:
Understanding HTML Attributes and Elements: HTML (HyperText Markup Language) forms the foundation of every website. Whether you’re building a personal blog, an eCommerce store, or a business portfolio, understanding HTML elements and attributes is your first step toward mastering web development. In this post, we’ll break down what HTML elements and attributes are, how they work together, and provide clear examples to help you learn fast.
What Are HTML Elements?
An HTML element is the basic building block of a web page. Every visible and structural part of a website such as text, images, links, or forms is created using HTML elements.
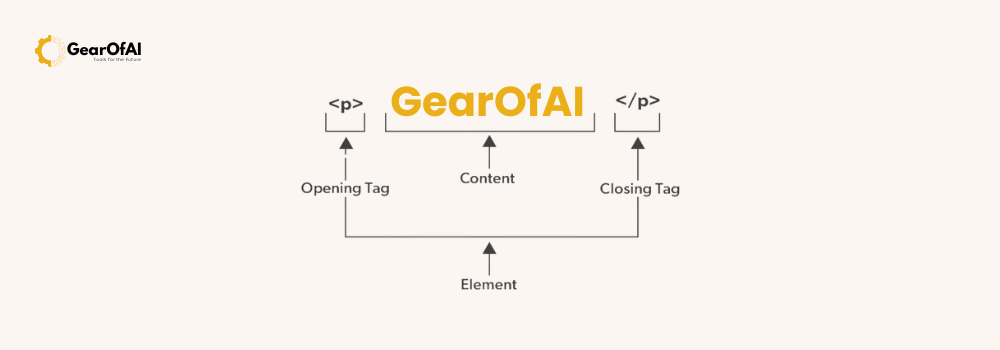
Each element usually consists of three parts:
- Opening tag – defines the start of the element.
- Content – the actual text or media displayed.
- Closing tag – indicates the end of the element.
Example:
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
<p>is the opening tagThis is a paragraph.is the content</p>is the closing tag
Together, these make up one HTML element.
Types of HTML Elements
HTML elements can be divided into two main types:
1. Block-Level Elements
These elements always start on a new line and take up the full width available. They are used to structure the layout of a page.
Examples:
<div>Container</div>
<p>Paragraph text</p>
<h1>Main heading</h1>
<section>Section content</section>
Block-level elements are great for organizing your web page into sections, making your content readable and structured.

2. Inline Elements
Inline elements do not start on a new line and only take up as much width as necessary. They are used for formatting text within a block-level container.
Examples:
<a href="#">Link</a>
<strong>Bold text</strong>
<em>Italic text</em>
<span>Inline container</span>
Inline elements are commonly used for links, emphasized words, or small design tweaks inside larger content areas.
What Are HTML Attributes?
Attributes provide additional information about HTML elements.
They appear inside the opening tag and are written as name-value pairs.
Example:
<img src="logo.png" alt="Company Logo" width="200" height="100">
Here’s what each attribute means:
srcspecifies the image file path.altprovides alternative text (important for accessibility and SEO).widthandheightdefine the image’s size.
Attributes are what give elements more power and flexibility.

Common HTML Attributes You Should Know
| Attribute | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
id | Gives an element a unique identifier. | <div id="main"></div> |
class | Groups elements for styling with CSS. | <p class="intro">...</p> |
style | Adds inline CSS directly to an element. | <h1 style="color:blue;">Hello</h1> |
title | Adds a tooltip when hovered. | <a title="Go to homepage">Home</a> |
href | Defines a link’s destination. | <a href="https://gearofai.com">Visit GearOfAI</a> |
src | Specifies the source of an image or video. | <img src="photo.jpg"> |
alt | Provides alternative text for images. | <img alt="Nature photo"> |
Boolean Attributes
Some attributes don’t need a value their presence alone means they’re “true.” These are called Boolean attributes.
Example:
<input type="checkbox" checked>
<input type="text" disabled>
Here:
checkedmeans the checkbox is already selected.disabledmeans the text box cannot be edited.
You don’t need to write checked="checked"; just writing checked works fine.
Global Attributes (Work on All Elements)
Some attributes can be applied to any HTML element. These are known as global attributes.
Common global attributes include:
idclassstyletitledata-*(used for custom data in JavaScript)
Example:
<div id="intro" class="highlight" title="Introduction section">
Welcome to GearOfAI tutorials!
</div>

This element uses three global attributes together.
Nesting HTML Elements
You can also nest (place) one element inside another to build complex layouts.
Example:
<div>
<h2>About Us</h2>
<p>Welcome to <strong>GearOfAI</strong>, your home for web development tutorials.</p>
</div>
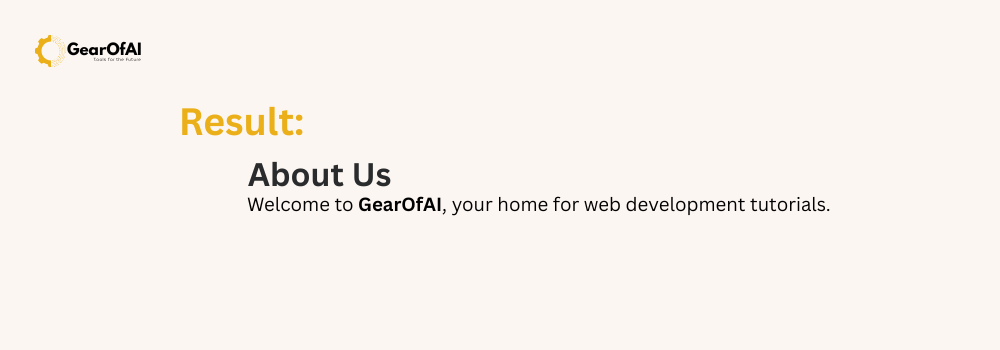
Here, the <p> tag is nested inside <div>, and <strong> is nested inside <p>.
This structure helps browsers understand the relationship between elements and how to display them properly.
HTML Attributes vs. CSS Properties
Although attributes can style elements using style, it’s better to use CSS files for clean, scalable design.
Example (Not Recommended):
<p style="color:red; font-size:20px;">This is inline styling</p>
Better Practice:
<p class="intro-text">This is styled using CSS</p>
And in your CSS file:
.intro-text {
color: red;
font-size: 20px;
}

This makes your code cleaner and easier to maintain.
HTML Attributes and Accessibility
Using attributes like alt, title, aria-label, and role helps make websites accessible to everyone, including users with screen readers.
Example:
<img src="dog.jpg" alt="A happy brown dog playing in the park">
The alt attribute describes the image to visually impaired users improving accessibility and SEO.
Example: Putting It All Together
Here’s a small webpage example combining everything you’ve learned:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Understanding HTML Elements and Attributes</title>
</head>
<body>
<header>
<h1>Welcome to GearOfAI!</h1>
<p>Your trusted source for learning web development and the best AI tools.</p>
</header>
<main>
<section id="intro" class="content-section">
<h2>About HTML</h2>
<p>HTML is the standard language used to build the structure of web pages.</p>
<img src="html-example.png" alt="HTML code example">
</section>
<section>
<h2>Learn More</h2>
<a href="https://gearofai.com/tutorials">Explore Tutorials</a>
</section>
</main>
<footer>
<p>Contact us: <a href="mailto:info@gearofai.com">info@gearofai.com</a></p>
</footer>
</body>
</html>

Why Understanding HTML Elements & Attributes Matters
Learning HTML gives you control over how your website looks and works.
Once you master this, you’ll find CSS and JavaScript much easier to understand.
At GearOfAI, we believe the best developers start with strong basics. Whether you’re learning AI-powered website builders or manual coding, understanding these fundamentals will set you apart.
Conclusion
HTML elements and attributes are the foundation of web development. They define what you see on a web page and how it behaves. Once you grasp how they work, you can confidently move to advanced topics like CSS styling, JavaScript interactivity, and even AI-assisted design tools that make website creation faster and smarter.